2010年1月28日木曜日
いろいろな気候インデックスとの相関
*
*
NOAA ESRLの
Linear Correlations in Atmospheric Seasonal/Monthly Averages
http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/data/correlation/というページで各種気候インデックスといろいろな物理量の相関がプロットできる。
NINO3.4と表面温度の相関 (12月から2月)
日本は暖冬傾向だが、北日本でははっきりしない。
参考:気象庁
北極振動と表面温度の相関 (12月から2月)
日本は正の相関である。つまり北極振動が負だと寒冬の傾向がある。
参考:気象庁
*
NOAA ESRLの
Linear Correlations in Atmospheric Seasonal/Monthly Averages
http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/data/correlation/というページで各種気候インデックスといろいろな物理量の相関がプロットできる。
NINO3.4と表面温度の相関 (12月から2月)
日本は暖冬傾向だが、北日本でははっきりしない。
参考:気象庁
北極振動と表面温度の相関 (12月から2月)
日本は正の相関である。つまり北極振動が負だと寒冬の傾向がある。
参考:気象庁
2010年1月24日日曜日
北極振動 気圧場
*
*
2008年と2009年の気圧場(1000hpa Geopotential height)を比較する。
2009年は北極振動のパターンと逆の符号(負のフェーズ)の傾向が強い。
以下プログラム。
を使用。
データはOpendapとい仕組みでNOAAからNCEP/NCARのデータを取得
*
2008年と2009年の気圧場(1000hpa Geopotential height)を比較する。
2009年は北極振動のパターンと逆の符号(負のフェーズ)の傾向が強い。
以下プログラム。
を使用。
データはOpendapとい仕組みでNOAAからNCEP/NCARのデータを取得
from grads.ganum import GaNum # for python interface for grads
from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap # for Basemap toolkit
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
for nyear in [2008,2009]:
# data import using python interface for grads
ga = GaNum(Bin='grads')
fh=ga.open("http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/thredds/dodsC/Datasets/ncep.reanalysis.derived/pressure/hgt.mon.mean.nc") # data open
ga("set time dec%(nyear)s" % locals())
ga("set lat 0 90")
ga("q file")
ga("set lev 1000") # 1000 hpa
hgt=ga.exp("hgt")
del ga
lat=hgt.grid.lat
lon=hgt.grid.lon
# map
fig=plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_axes([0.1,0.1,0.8,0.8])
map = Basemap(projection='nplaea',boundinglat=10,lon_0=135,resolution='i')
map.drawcoastlines()
map.drawmapboundary()
lons,lats=np.meshgrid(lon[:],lat[:])
x,y=map(lons,lats)
map.fillcontinents()
cz=map.contour(x,y,hgt[:,:],np.arange(-100,300,20))
plt.clabel(cz,fmt="%3.0f")
plt.title("Geopotential height (m): Dec %(nyear)s " % locals())
plt.savefig("gpt_%(nyear)s.png" % locals())
plt.show()
2010年1月23日土曜日
北極振動 Rで統計 グラフ編
*
*
前回の続き
前回の続き
#boxplot去年の12月の値は「外れ値」にはなっていない
scripts="""
png(’boxplot.png’)
boxplot(rdatain)
dev.off()
"""
r(scripts)
#hist
scripts="""
png('hist.png')
hist(rdatain,seq(-4, 4, 0.4),prob=TRUE)
x<-seq(-4, 4, 0.2)
lines(x, dnorm(x, mean=mean(rdatain), sd=sqrt(var(rdatain))), lty=3)
dev.off()
"""
a=r(scripts)
#cdf plot
scripts="""
png('cdf.png')
plot(ecdf(rdatain), do.points=FALSE, verticals=TRUE)
x<-seq(-4, 4, 0.01)
lines(x, pnorm(x, mean=mean(rdatain), sd=sqrt(var(rdatain))), lty=3)
dev.off()
"""
r(scripts)
#qqplot
scripts="""
png('qqplot.png')
qqnorm(rdatain)
qqline(rdatain)
dev.off()
"""
r(scripts)
正規分布より分布がせまい。
2010年1月21日木曜日
北極振動 Rで統計
北極振動 12月だけを抜き出しの続き
12月のデータだけ抜き出して、Rで統計処理する。 Rpy2を使う。
まずは以下のように準備。readAOとpickup_monthは以前作ったもの。
AO_rpy2.py
from readAO import readAO # read AO data
from pick_month import pick_month # pick month
#
import scikits.timeseries as ts
#
import rpy2.robjects as robjects
# read AO data
AOindex_series=readAO()
# pickup December
AOindex_dec=pick_month(AOindex_series,month=12)
#remove missig value
data=AOindex_dec[AOindex_dec.mask==False].data
# for R
rdata=robjects.FloatVector(data)
robjects.globalEnv["rdatain"] = rdata
r=robjects.r
それで、
a=r('summary(rdatain)')
または
a=r.summary(rdata)
または
summary=r['summary']
a=summary(rdata)
a=summary(rdata)
いずれも同じ結果
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
-3.41300 -1.24200 -0.08762 -0.19740 0.82490 2.28200
print a[0]
-3.413
print a.names
[1] "Min." "1st Qu." "Median" "Mean" "3rd Qu." "Max."
b=a.r["Mean"]
print b
Mean
-0.1974
b[0]
-0.19739999999999999
print a.subset(1)
Min.
-3.413
参考
Rで統計: データ集合中の最大、最小、平均、中央値 - summary()関数http://www.yukun.info/blog/2008/09/r-summary-mean-median.html
2010年1月19日火曜日
北極振動 12月だけを抜き出し
続き
北極振動
北極振動 年平均
AO 各年ごとにプロット および 気候学平均
北極振動の時系列から12月だけを抜き出す。
以下、プログラム。
pick_month.py
北極振動
北極振動 年平均
AO 各年ごとにプロット および 気候学平均
北極振動の時系列から12月だけを抜き出す。
以下、プログラム。
pick_month.py
from readAO import readAO
#
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scikits.timeseries as ts
import scikits.timeseries.lib.plotlib as tpl
def pick_month(series,month):
""" pick time series only month==month
"""
mask=(series.dates.month==month)
out=series[mask].asfreq("A")
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
AOindex_series=readAO()
# pickup December
AOindex_dec=pick_month(AOindex_series,month=12)
#plot
fig = tpl.tsfigure()
fsp = fig.add_tsplot(111)
fsp.tsplot(AOindex_dec, 'r-')
plt.xlabel("YEAR")
plt.ylabel("AO index")
plt.savefig("AOindex_dec.png")
plt.show()
AO 各年ごとにプロット および 気候学平均
続き
北極振動
北極振動 年平均
AOを各年毎にプロット(黒線)
2009年だけ赤線
気候学的平均(各月ごと、青線)
2009年の12月は異常に値が小さかったことがわかる。
以下プログラム。
北極振動
北極振動 年平均
AOを各年毎にプロット(黒線)
2009年だけ赤線
気候学的平均(各月ごと、青線)
2009年の12月は異常に値が小さかったことがわかる。
以下プログラム。
plot_AO_season.py
from readAO import readAO
#
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scikits.timeseries as ts
import scikits.timeseries.lib.plotlib as tpl
AOindex_series=readAO()
# to seasonal
AOindex_season=ts.extras.convert_to_annual(AOindex_series)
#plot each year
fig = tpl.tsfigure()
fsp = fig.add_tsplot(111)
for n in range(AOindex_season.shape[0]):
series = ts.time_series(AOindex_season[n,:], start_date=ts.Date(freq="m",year=1990,month=1),length=12)
lstyle='k-'
if AOindex_season.dates.year[n] == 2009:
lstyle='r-'
fsp.tsplot(series, lstyle)
# climatological average
AOindex_average = ts.time_series(np.mean(AOindex_season,axis=0), start_date=ts.Date(freq="m",year=1990,month=1),length=12)
fsp.tsplot(AOindex_average, 'b-',linewidth=2)
fsp.xaxis.set_ticklabels(["Jan"]) # dirty trick for plot
plt.savefig("AO_season.png")
plt.show()
2010年1月18日月曜日
Sageで数学 素数
Sageで素数を遊んでみる。
sage: A=Primes()
sage: A.first()
2
sage: A.next(2)
3
sage: A.next(3)
5
sage: A.next(5)
7
sage: A.next(4)
5
sage: A.unrank(0)
2
sage: A.unrank(4) #Returns the 4-th prime number.
11
sage: A.unrank(100)
547sage: 17 in A
True
sage: A.cardinality() # Counts the elements of the enumerated set.
+Infinity
sage: prime_pi(548) # Return the number of primes <=549
101
sage: plot(prime_pi,1,600)
2010年1月13日水曜日
北極振動 年平均
続き
北極振動
年平均をつくる。
前回のreadAO.pyを用いる。
北極振動
年平均をつくる。
前回のreadAO.pyを用いる。
from readAO import readAO
#
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scikits.timeseries as ts
import scikits.timeseries.lib.plotlib as tpl
AOindex_series=readAO()
# to annual mean
AOindex_annual=ts.convert(AOindex_series,'A',func=np.ma.mean)
#plot
fig = tpl.tsfigure()
fsp = fig.add_tsplot(111)
fsp.tsplot(AOindex_annual, 'r-+')
istart=fsp.get_xlim()[0]
iend=ts.Date('A','2010').value
fsp.set_xlim(istart,iend)
plt.xlabel("YEAR")
plt.ylabel("AO index")
plt.savefig("AOindex_anu.png")
plt.show()
2010年1月12日火曜日
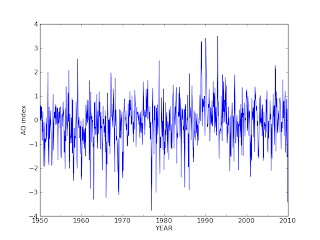
北極振動
最近、寒いのは北極振動が負になっているのが関係しているらしい。
北極振動 wikipedia
http://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%8C%97%E6%A5%B5%E6%8C%AF%E5%8B%95
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arctic_oscillation
AOのデータは以下から入手できる。
http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/precip/CWlink/daily_ao_index/ao.shtml
プロットしてみる
北極振動 wikipedia
http://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%8C%97%E6%A5%B5%E6%8C%AF%E5%8B%95
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arctic_oscillation
AOのデータは以下から入手できる。
http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/precip/CWlink/daily_ao_index/ao.shtml
プロットしてみる
以下プログラム(python)。scikits.timeseriesを使っている。
readAO.py
def readAO():
"import monthly AO data"
import numpy as np
import scikits.timeseries as ts
# data is downloaded from http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/precip/CWlink/daily_ao_index/monthly.ao.index.b50.current.ascii
f=open("monthly.ao.index.b50.current.ascii",'r')
data=np.loadtxt(f)
f.close()
AOindex=data[:,2]
year=data[:,0]
month=data[:,1]
# make time series
tbeginmonth=str(int(year[0]))+"-"+str(int(month[0]))
dbeginmonth=ts.Date('M', tbeginmonth)
AOindex_series=ts.time_series(AOindex,start_date=dbeginmonth,freq='M',mask=(AOindex<-99.))
return AOindex_series
##################################
if __name__ == '__main__':
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scikits.timeseries as ts
import scikits.timeseries.lib.plotlib as tpl
from datetime import datetime
AOindex_series=readAO()
fig = tpl.tsfigure()
fsp = fig.add_tsplot(111)
fsp.tsplot(AOindex_series, '-')
istart=fsp.get_xlim()[0]
iend=ts.Date('M','2010-1').value
fsp.set_xlim(istart,iend)
plt.xlabel("YEAR")
plt.ylabel("AO index")
plt.savefig("AOindex.png")
plt.show()
登録:
投稿 (Atom)